129 lines
3.3 KiB
Markdown
129 lines
3.3 KiB
Markdown
|
|
---
|
|||
|
|
title: Breadth First Search (BFS)
|
|||
|
|
---
|
|||
|
|
## Breadth First Search (BFS)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Breadth First Search is one of the most simple graph algorithms. It traverses the graph by first checking the current node and then expanding it by adding its successors to the next level. The process is repeated for all nodes in the current level before moving to the next level. If the solution is found the search stops.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### Visualisation
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
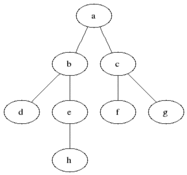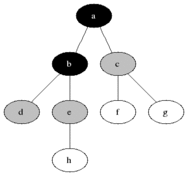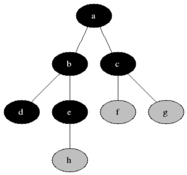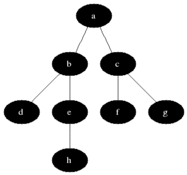
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### Evaluation
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Space Complexity: O(n)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Worse Case Time Complexity: O(n)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Breadth First Search is complete on a finite set of nodes and optimal if the cost of moving from one node to another is constant.
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### C++ code for BFS implementation
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```cpp
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// Program to print BFS traversal from a given
|
|||
|
|
// source vertex. BFS(int s) traverses vertices
|
|||
|
|
// reachable from s.
|
|||
|
|
#include<iostream>
|
|||
|
|
#include <list>
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
using namespace std;
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// This class represents a directed graph using
|
|||
|
|
// adjacency list representation
|
|||
|
|
class Graph
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
int V; // No. of vertices
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// Pointer to an array containing adjacency
|
|||
|
|
// lists
|
|||
|
|
list<int> *adj;
|
|||
|
|
public:
|
|||
|
|
Graph(int V); // Constructor
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// function to add an edge to graph
|
|||
|
|
void addEdge(int v, int w);
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// prints BFS traversal from a given source s
|
|||
|
|
void BFS(int s);
|
|||
|
|
};
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Graph::Graph(int V)
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
this->V = V;
|
|||
|
|
adj = new list<int>[V];
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v’s list.
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
void Graph::BFS(int s)
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
|
|||
|
|
bool *visited = new bool[V];
|
|||
|
|
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
|
|||
|
|
visited[i] = false;
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// Create a queue for BFS
|
|||
|
|
list<int> queue;
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// Mark the current node as visited and enqueue it
|
|||
|
|
visited[s] = true;
|
|||
|
|
queue.push_back(s);
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// 'i' will be used to get all adjacent
|
|||
|
|
// vertices of a vertex
|
|||
|
|
list<int>::iterator i;
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
while(!queue.empty())
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
// Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it
|
|||
|
|
s = queue.front();
|
|||
|
|
cout << s << " ";
|
|||
|
|
queue.pop_front();
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued
|
|||
|
|
// vertex s. If a adjacent has not been visited,
|
|||
|
|
// then mark it visited and enqueue it
|
|||
|
|
for (i = adj[s].begin(); i != adj[s].end(); ++i)
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
if (!visited[*i])
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
visited[*i] = true;
|
|||
|
|
queue.push_back(*i);
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// Driver program to test methods of graph class
|
|||
|
|
int main()
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
|
|||
|
|
Graph g(4);
|
|||
|
|
g.addEdge(0, 1);
|
|||
|
|
g.addEdge(0, 2);
|
|||
|
|
g.addEdge(1, 2);
|
|||
|
|
g.addEdge(2, 0);
|
|||
|
|
g.addEdge(2, 3);
|
|||
|
|
g.addEdge(3, 3);
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
cout << "Following is Breadth First Traversal "
|
|||
|
|
<< "(starting from vertex 2) \n";
|
|||
|
|
g.BFS(2);
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
return 0;
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### More Information:
|
|||
|
|
<!-- Please add any articles you think might be helpful to read before writing the article -->
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
<a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/computer-science/data-structures/graphs/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Graphs</a>
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
<a href='https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/algorithms/graph-algorithms/depth-first-search/index.md' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Depth First Search (DFS)</a>
|