182 lines
6.1 KiB
Markdown
182 lines
6.1 KiB
Markdown
|
|
---
|
|||
|
|
title: OAuth2 Protocol
|
|||
|
|
localeTitle: OAuth2协议
|
|||
|
|
---
|
|||
|
|
## OAuth 2.0
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
[OAuth 2.0](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749)是一种行业标准授权协议,它使第三方应用程序能够代表资源所有者(系统用户)有限地访问资源
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
OAuth广泛应用于Google,Facebook,Slack等许多主要互联网公司
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**目录**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* 基础知识
|
|||
|
|
* 协议流程
|
|||
|
|
* 授权授权类型
|
|||
|
|
* 参考
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 基础知识
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### [角色](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749#section-1.1)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* **资源所有者** : 使用产品或服务的人(例如:您是Google帐户中的资源所有者)
|
|||
|
|
* **资源服务器** : 服务器托管客户受保护的数据(例如:托管电子邮件的Gmail)
|
|||
|
|
* **客户** : 应用程序请求访问资源服务器中的数据
|
|||
|
|
* **授权服务器** : 处理授权请求的服务器,向请求客户端发出访问令牌。此服务器可以与资源服务器相同,也可以是单独的服务器
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### 令牌
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
OAuth 2.0中定义了两种类型的令牌
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* **[访问令牌](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749#section-1.4)** : 访问令牌是OAuth的关键部分,因为它允许从任何拥有此令牌的应用程序访问用户数据。此令牌具有由授权服务器定义的有限生命周期。
|
|||
|
|
* **[刷新令牌](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749#section-1.5)** : 此令牌作为访问令牌的一部分发布,因为访问令牌的生命周期有限,有时客户端应用程序需要访问用户数据更长时间(例如:集成服务),在这种情况下,客户端应用程序可以请求刷新令牌,这允许它们更新访问令牌以获得需要重新授权用户的新版本。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### [访问令牌范围](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749#section-3.3)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
客户端授权请求中的scope参数,允许客户端应用程序指定他们想要访问的资源或数据类型,可用范围由授权服务器确定,一旦授权,请求的范围附加到访问令牌,给定访问令牌限制访问用户数据而不是完全访问权限。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### [协议流程](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749#section-1.2)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 授权授权类型
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
OAuth2定义了4种类型的授权,以根据客户端的性质获取访问令牌。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* 授权码
|
|||
|
|
* 隐含流动
|
|||
|
|
* 资源所有者凭据
|
|||
|
|
* 客户端凭据
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### 授权代码授予
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
客户性质:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
能够安全存储客户端密钥(通常是Web服务器)的客户端可以使用此授权进行授权。这还允许通过刷新令牌的帮助获得长期访问令牌。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
例如:Web应用程序请求访问Google帐户用户的信息
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
摘要流程
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
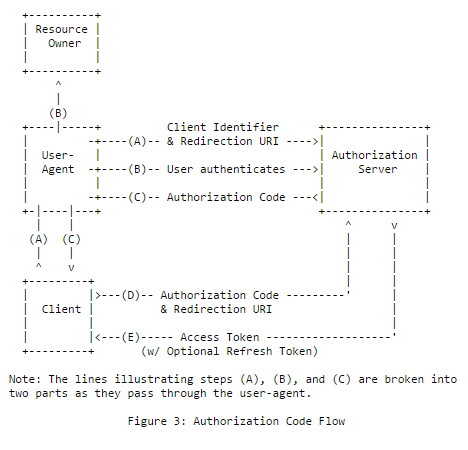
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
代码示例:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
授权请求
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
GET /oauth2/authorize?response_type=code
|
|||
|
|
&client_id=client123&scope=profile
|
|||
|
|
&redirect_uri=https://client.com/callback HTTP/1.1
|
|||
|
|
Host: auth.server.com
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
|
|||
|
|
Location: https://client.com/callback#code=sb8s6doy9bsd9sd&state=abcde
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
发布接收授权代码,用代码向授权服务器发出请求,
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
POST /oauth2/token HTTP/1.1
|
|||
|
|
Host: auth.server.com
|
|||
|
|
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
grant_type=authorization_code
|
|||
|
|
&code=sb8s6doy9bsd9sd
|
|||
|
|
&redirect_uri=https://client.com/callback
|
|||
|
|
&client_id=client123
|
|||
|
|
&client_secret=secret
|
|||
|
|
&scope=profile
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
响应
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
|
|||
|
|
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
|
|||
|
|
Cache-Control: no-store
|
|||
|
|
Pragma: no-cache
|
|||
|
|
{
|
|||
|
|
"access_token":"gsi8d6fosb9d6fos6df",
|
|||
|
|
"token_type":"bearer",
|
|||
|
|
"expires_in":3600
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### 隐含流动
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
客户性质:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在浏览器中运行的客户端应用程序,通常是前端应用程序(例如:SPA)。此Grant不会发出刷新令牌。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
例如:在浏览器中运行的前端javascript应用程序
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
摘要流程:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
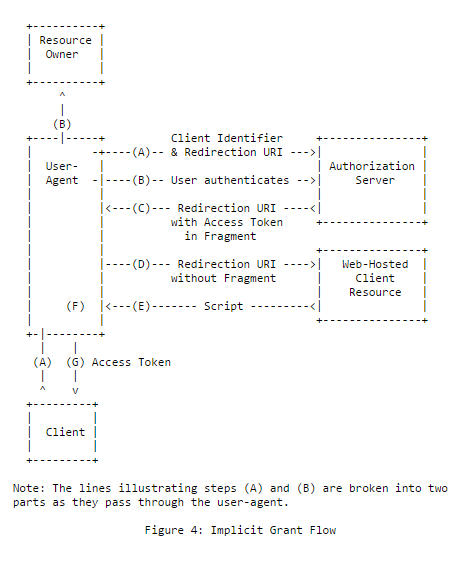
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
代码示例:
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
GET /oauth2/authorize?response_type=token
|
|||
|
|
&client_id=client123
|
|||
|
|
&redirect_uri=https://client.com/callback HTTP/1.1
|
|||
|
|
Host: auth.server.com
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
|
|||
|
|
Location: https://client.com/callback#access_token=98y2b38&token_type=bearer&expires_in=3600&state=abcde
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### 资源所有者凭据
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
客户性质:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在此流程中,资源所有者与客户端共享其凭据(密码),然后与授权服务器共享,因此当它们是客户端应用程序和授权服务器之间的绝对信任时,将使用此授权。因此,第三方客户端应用程序通常不允许此流程。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
例如:使用此流程的Facebook移动应用程序通过Facebook Server进行授权
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
摘要流程:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
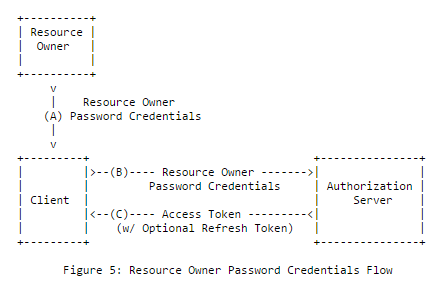
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
代码示例:
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
POST /oauth2/token HTTP/1.1
|
|||
|
|
Host: auth.server.com
|
|||
|
|
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
grant_type=password
|
|||
|
|
&username=john
|
|||
|
|
&password=abcde
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### 客户端凭据流
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
客户性质:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
当客户端本身是资源所有者时(即客户端想要访问其使用限制或与其相关的信息),将使用此类授权。此流程中没有最终用户授权。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
例如:客户端应用程序从谷歌服务器请求非用户数据(例如:时区,地图等)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
摘要流程:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
代码示例:
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
POST /oauth2/token HTTP/1.1
|
|||
|
|
Host: auth.server.com
|
|||
|
|
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
grant_type=client_credentials
|
|||
|
|
&client_id=client123
|
|||
|
|
&client_secret=xyz123
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 参考
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
有关更多阅读,请参阅
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* [OAuth2草案](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749)
|
|||
|
|
* [了解OAuth2](http://www.bubblecode.net/en/2016/01/22/understanding-oauth2/)
|
|||
|
|
* [创建自己的openId连接服务器](http://kevinchalet.com/2016/07/13/creating-your-own-openid-connect-server-with-asos-choosing-the-right-flows/)
|