125 lines
3.2 KiB
Markdown
125 lines
3.2 KiB
Markdown
|
|
---
|
||
|
|
title: Breadth First Search (BFS)
|
||
|
|
localeTitle: Primera búsqueda de amplitud (BFS)
|
||
|
|
---
|
||
|
|
## Primera búsqueda de amplitud (BFS)
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Breadth First Search es uno de los algoritmos gráficos más simples. Atraviesa el gráfico al verificar primero el nodo actual y luego expandirlo agregando sus sucesores al siguiente nivel. El proceso se repite para todos los nodos en el nivel actual antes de pasar al siguiente nivel. Si se encuentra la solución, la búsqueda se detiene.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Visualización
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
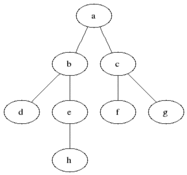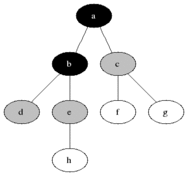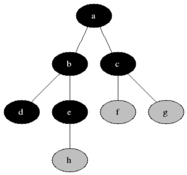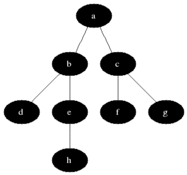
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Evaluación
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Complejidad del espacio: O (n)
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Peor caso complejidad del tiempo: O (n)
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
La primera búsqueda de amplitud se completa en un conjunto finito de nodos y es óptima si el costo de pasar de un nodo a otro es constante.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
### Código C ++ para implementación BFS
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```cpp
|
||
|
|
// Program to print BFS traversal from a given
|
||
|
|
// source vertex. BFS(int s) traverses vertices
|
||
|
|
// reachable from s.
|
||
|
|
#include<iostream>
|
||
|
|
#include <list>
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
using namespace std;
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
// This class represents a directed graph using
|
||
|
|
// adjacency list representation
|
||
|
|
class Graph
|
||
|
|
{
|
||
|
|
int V; // No. of vertices
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
// Pointer to an array containing adjacency
|
||
|
|
// lists
|
||
|
|
list<int> *adj;
|
||
|
|
public:
|
||
|
|
Graph(int V); // Constructor
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
// function to add an edge to graph
|
||
|
|
void addEdge(int v, int w);
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
// prints BFS traversal from a given source s
|
||
|
|
void BFS(int s);
|
||
|
|
};
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Graph::Graph(int V)
|
||
|
|
{
|
||
|
|
this->V = V;
|
||
|
|
adj = new list<int>[V];
|
||
|
|
}
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
|
||
|
|
{
|
||
|
|
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v's list.
|
||
|
|
}
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
void Graph::BFS(int s)
|
||
|
|
{
|
||
|
|
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
|
||
|
|
bool *visited = new bool[V];
|
||
|
|
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
|
||
|
|
visited[i] = false;
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
// Create a queue for BFS
|
||
|
|
list<int> queue;
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
// Mark the current node as visited and enqueue it
|
||
|
|
visited[s] = true;
|
||
|
|
queue.push_back(s);
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
// 'i' will be used to get all adjacent
|
||
|
|
// vertices of a vertex
|
||
|
|
list<int>::iterator i;
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
while(!queue.empty())
|
||
|
|
{
|
||
|
|
// Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it
|
||
|
|
s = queue.front();
|
||
|
|
cout << s << " ";
|
||
|
|
queue.pop_front();
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
// Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued
|
||
|
|
// vertex s. If a adjacent has not been visited,
|
||
|
|
// then mark it visited and enqueue it
|
||
|
|
for (i = adj[s].begin(); i != adj[s].end(); ++i)
|
||
|
|
{
|
||
|
|
if (!visited[*i])
|
||
|
|
{
|
||
|
|
visited[*i] = true;
|
||
|
|
queue.push_back(*i);
|
||
|
|
}
|
||
|
|
}
|
||
|
|
}
|
||
|
|
}
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
// Driver program to test methods of graph class
|
||
|
|
int main()
|
||
|
|
{
|
||
|
|
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
|
||
|
|
Graph g(4);
|
||
|
|
g.addEdge(0, 1);
|
||
|
|
g.addEdge(0, 2);
|
||
|
|
g.addEdge(1, 2);
|
||
|
|
g.addEdge(2, 0);
|
||
|
|
g.addEdge(2, 3);
|
||
|
|
g.addEdge(3, 3);
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
cout << "Following is Breadth First Traversal "
|
||
|
|
<< "(starting from vertex 2) \n";
|
||
|
|
g.BFS(2);
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
return 0;
|
||
|
|
}
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
#### Más información:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
[Graficas](https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/computer-science/data-structures/graphs/index.md)
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
[Primera búsqueda de profundidad (DFS)](https://github.com/freecodecamp/guides/tree/master/src/pages/algorithms/graph-algorithms/depth-first-search/index.md)
|