---
title: Reading Box Plots
---
## Reading Box Plots
Box Plots might seem unintuitive at first glance, but they are a great way to convey a lot of information of a compact format. Here's how you can read the informations contained in a
Box Plot:
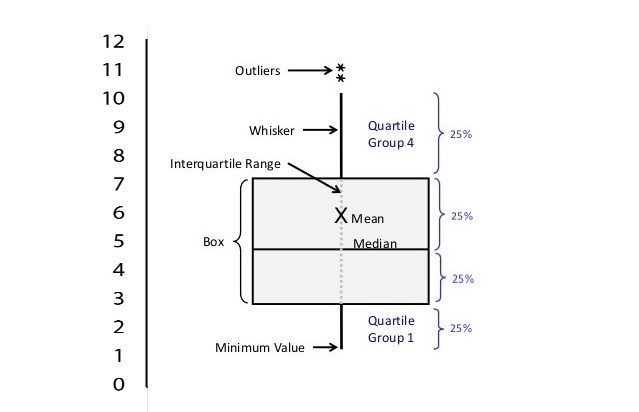
The Box Plot has several elements that we can recognize:
* The box, which is bisected in two parts
* Two whiskers, above and below the box
* Possibly some scattered points: the outliers
Each section of the box plot represents the interval of a quartile of the population of data. What this means, is that 25% of the data lies within the two ends of the lower whisker, 25% within the interval spanned by the bottom of the box and the median line, 25% within the median and the top of the box, and 25% in the upper whisker. Any statistical outlier is represented as a point outside of the box.
In the example reported above we would have (using approximate numerical values):
* a quarter of the data between 1 and 3 (lower whisker)
* a quarter of the data between 3 and 5 (lower part of the box)
* a quarter of the data between 5 and 7.5 (upper part of the box)
* a quarter of the data between 7.5 and 10 (upper whisker)
* two outlier points above the boxplot
Notice that the line that bisects the box represents the **Median** (50th percentile) and **not the Mean**.
#### More Information:
For more informations:
* Wikipedia: Box Plot
* Khan Academy: reading Box Plots(video)