3.6 KiB
| title |
|---|
| AVL Trees |
AVL Trees
An AVL tree is a subtype of binary search tree. Named after its inventors Adelson, Velskii and Landis, AVL trees have the property of dynamic self-balancing in addition to all the properties exhibited by Binary Search Trees (BSTs).
A BST is a data structure composed of nodes. It has the following guarantees:
- Each tree has a root node (at the top).
- The root node has zero, one or two child nodes.
- Each child node has zero, one or two child nodes, and so on.
- For each node, the value of its left descendants are less than the current node, which is less than the value of the right descendants.
AVL trees have some additional guarantees:
- The difference between the depth of right and left sub-trees cannot be more than one. In order to maintain this guarantee, an implementation of an AVL will include an algorithm to rebalance the tree when adding an additional element would upset this guarantee.
- The height of an AVL tree is always
log(n)wherenis the number of nodes in the tree.
AVL trees have a worst case lookup, insert, and delete time of O(log(n)).
AVL Tree Rotations
In an AVL tree, after performing an operation like insertion or deletion, we need to check the balance factor of every node in the tree. If every node satisfies the balance factor condition, then we conclude the operation; otherwise, we must make it balanced.
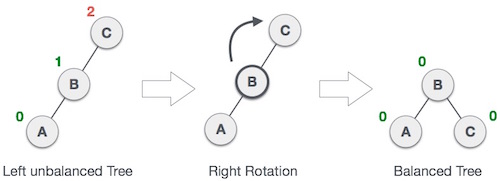
Single Right Rotation (RR Rotation)
In RR Rotation every node moves one position to right from the current position.
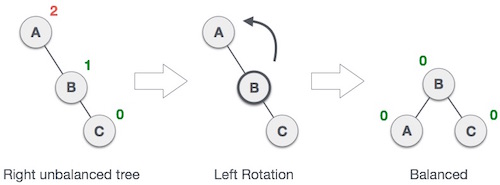
Single Left Rotation (LL Rotation)
In LL Rotation every node moves one position to left from the current position.
Left Right Rotation (LR Rotation)
The LR Rotation is combination of single left rotation followed by single right rotation. In LR Rotation, first every node moves one position to left then one position to right from the current position.
Right Left Rotation (RL Rotation)
The RL Rotation is combination of single right rotation followed by single left rotation. In RL Rotation, first every node moves one position to right then one position to left from the current position.
AVL Insertion Process
Insertion in an AVL Tree are similar to a normal Binary Search Tree insertion. After inserting, you fix the AVL property using left or right rotations.
- If there is an imbalance in left child of right subtree, then you perform a left-right rotation.
- If there is an imbalance in left child of left subtree, then you perform a right rotation.
- If there is an imbalance in right child of right subtree, then you perform a left rotation.
- If there is an imbalance in right child of left subtree, then you perform a right-left rotation.
Time Analysis Of AVL Tree
AVL tree is binary search tree with additional property that difference between height of left sub-tree and right sub-tree of any node can’t be more than 1.
| Algorithm | Average | Worst case |
|---|---|---|
| Space | O(n) |
O(n) |
| Search | O(log(n)) |
O(log(n)) |
| Insert | O(log(n)) |
O(log(n)) |
| Delete | O(log(n)) |
O(log(n)) |
Application of AVL Trees
One beneficial use case for an AVL Tree is when you are designing a database where insertions and deletions are not performed frequently but often require look-ups