73 lines
2.6 KiB
Markdown
73 lines
2.6 KiB
Markdown
---
|
|
title: Euler's Method
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
# Euler's Method
|
|
|
|
The Euler's method is a first-order numerical procedure for solving ordinary differential equations (ODE) with a given initial value.
|
|
|
|
## The General Initial Value Problem
|
|
|
|
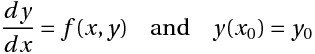
|
|
|
|
## Methodology
|
|
|
|
Euler's method uses the simple formula,
|
|
|
|
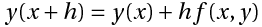
|
|
|
|
to construct the tangent at the point `x` and obtain the value of `y(x+h)`, whose slope is,
|
|
|
|
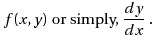
|
|
|
|
|
|
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pranabendra/articles/master/Euler-method/images/Euler.png" width="600">
|
|
|
|
|
|
In Euler's method, you can approximate the curve of the solution by the tangent in each interval (that is, by a sequence of short line segments), at steps of `h`.
|
|
|
|
<i>In general</i>, if you use small step size, the accuracy of approximation increases.
|
|
|
|
## General Formula
|
|
|
|
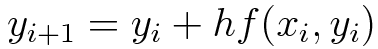
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
## Functional value at any point `b`, given by `y(b)`
|
|
|
|
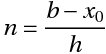
|
|
|
|
where,
|
|
* <b>n</b> = number of steps
|
|
* <b>h</b> = interval width (size of each step)
|
|
|
|
### Pseudocode
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
## Example
|
|
|
|
Find `y(1)`, given
|
|
|
|
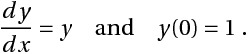
|
|
|
|
|
|
Solving analytically, the solution is <i><b>y = e<sup>x</sup></b></i> and `y(1)`= `2.71828`. (Note: This analytic solution is just for comparing the accuracy.)
|
|
|
|
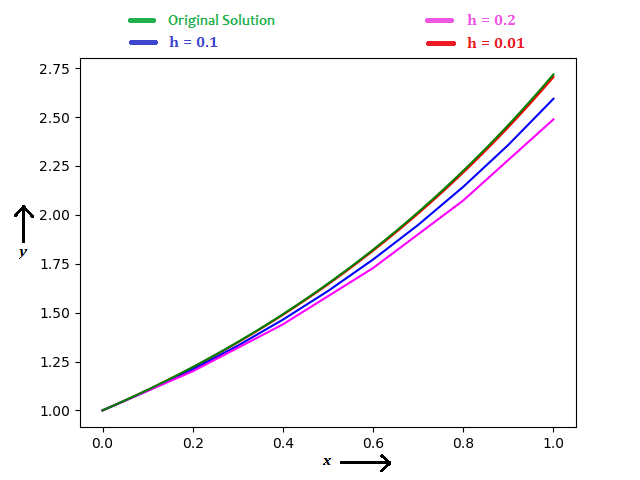
Using Euler's method, considering `h` = `0.2`, `0.1`, `0.01`, you can see the results in the diagram below.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
When `h` = `0.2`, `y(1)` = `2.48832` (error = 8.46 %)
|
|
|
|
When `h` = `0.1`, `y(1)` = `2.59374` (error = 4.58 %)
|
|
|
|
When `h` = `0.01`, `y(1)` = `2.70481` (error = 0.50 %)
|
|
|
|
You can notice, how accuracy improves when steps are small.
|
|
|
|
## More Information:
|
|
1. <a href='http://calculuslab.deltacollege.edu/ODE/7-C-1/7-C-1-h-c.html' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Numerical Methods for Solving Differential Equations</a>
|
|
2. <a href='https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler_method' target='_blank' rel='nofollow'>Euler's method</a>
|