2.6 KiB
| title |
|---|
| bitwise operator example |
Bitwise operators
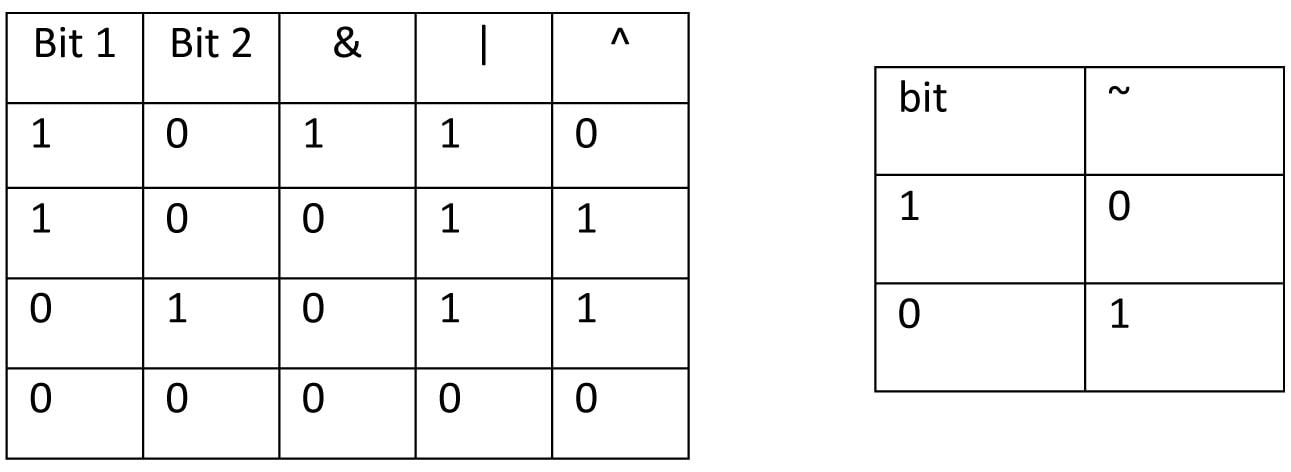
Truth table
The bitwise operators are similar to the logical operators, except that they work on a smaller scale -- binary representations of data. Any data can be converted to its binary equivalent. Though binary operators work at binary level but they are operated between normal decimal values only.
Types of Bitwise Operators
Bitwise OR
Bitwise OR is a binary operator (operates on two operands). It's denoted by |. The | operator compares corresponding bits of two operands. If either of the bits is 1, it gives 1. If not, it gives 0.
Bitwise AND
Bitwise AND is a binary operator (operates on two operands). It's denoted by &. The & operator compares corresponding bits of two operands. If both bits are 1, it gives 1. If either of the bits is not 1, it gives 0.
Bitwise Complement
Bitwise complement is an unary operator (works on only one operand). It is denoted by ~. The ~ operator inverts the bit pattern. It makes every 0 to 1, and every 1 to 0.
Bitwise XOR
Bitwise XOR is a binary operator (operates on two operands). It's denoted by ^. The ^ operator compares corresponding bits of two operands. If corresponding bits are different, it gives 1. If corresponding bits are same, it gives 0.
Left Shift
The left shift operator << shifts a bit pattern to the left by certain number of specified bits, and zero bits are shifted into the low-order positions.
Right Shift
The right shift operator >> shifts a bit pattern to the right by certain number of specified bits.If the number is a 2's complement signed number, the sign bit is shifted into the high-order positions.
Unsigned Right Shift
The unsigned right shift operator >>> shifts zero into the leftmost position.
Example bitwise operators :
int a = 60; /* 60 = 0011 1100 represents 60 in binary*/
int b = 13; /* 13 = 0000 1101 */
int c = 0;
c = a & b; /* 12 = 0000 1100 */
c = a | b; /* 61 = 0011 1101 */
c = a ^ b; /* 49 = 0011 0001 */
c = ~a; /*-61 = 1100 0011 :Invert all bits */
// shift operators : zeros are shifted in to replace the discarded bits
c = a << 2; /* 240 = 1111 0000 : Shift left 2 bits*/
c = a >> 2; /* 15 = 1111 */
c = a >>> 2; /* 15 = 0000 1111 : Zero fill right shift*/
FOR FURTHER INFORMATION: Click Here