7.0 KiB
| id | title | challengeType | forumTopicId | dashedName |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 587d8257367417b2b2512c7b | 將新元素添加到二叉搜索樹 | 1 | 301618 | add-a-new-element-to-a-binary-search-tree |
--description--
這一系列的挑戰將介紹樹形數據結構。 樹是計算機科學中一個重要的、通用的數據結構。 當然,它們的名稱來自這樣一個事實:當可視化時,它們看起來很像我們在自然界中熟悉的樹木。 樹數據結構從一個節點(通常稱爲根)開始,並從此處分支到其他節點,每個節點可能具有更多的子節點,依此類推。 數據結構通常以根節點爲頂點進行可視化;你可以把它想象成一棵倒過來的自然樹。
首先,讓我們描述一下我們將遇到的關於樹的一些常見術語。 根節點(root)是樹的頂部。 樹中的數據點稱爲節點(node)。 分支通向其他節點的節點稱爲分支通向的節點(即子節點)的父節點。 如你所料,其他更復雜的家庭術語也適用。 子樹指的是某一特定節點的所有後代,分支可稱爲邊,而葉子節點是位於樹的末端的且沒有子節點的節點。 最後,請注意,樹本質上是遞歸的數據結構。 也就是說,一個節點的任何子節點都是其自己的子樹的父節點,依此類推。 在爲常見的樹操作設計算法時,樹的遞歸性質很重要。
首先,我們將討論樹的一個特殊類型,即二叉樹。 實際上,我們將討論特定的二叉樹,即二叉搜索樹。 讓我們來看看這意味着什麼。 雖然樹形數據結構在一個節點上可以有任意數量的分支,但二叉樹每個節點只能有兩個分支。 此外,一個二叉搜索樹相對於其子子樹是有序的,即對於一個節點而言,其左子樹中每個節點的值都小於或等於該節點的值,而其右子樹中每個節點的值都大於或等於該節點的值。 爲了更好地理解這種關係,將這種關係形象化是非常有幫助的:
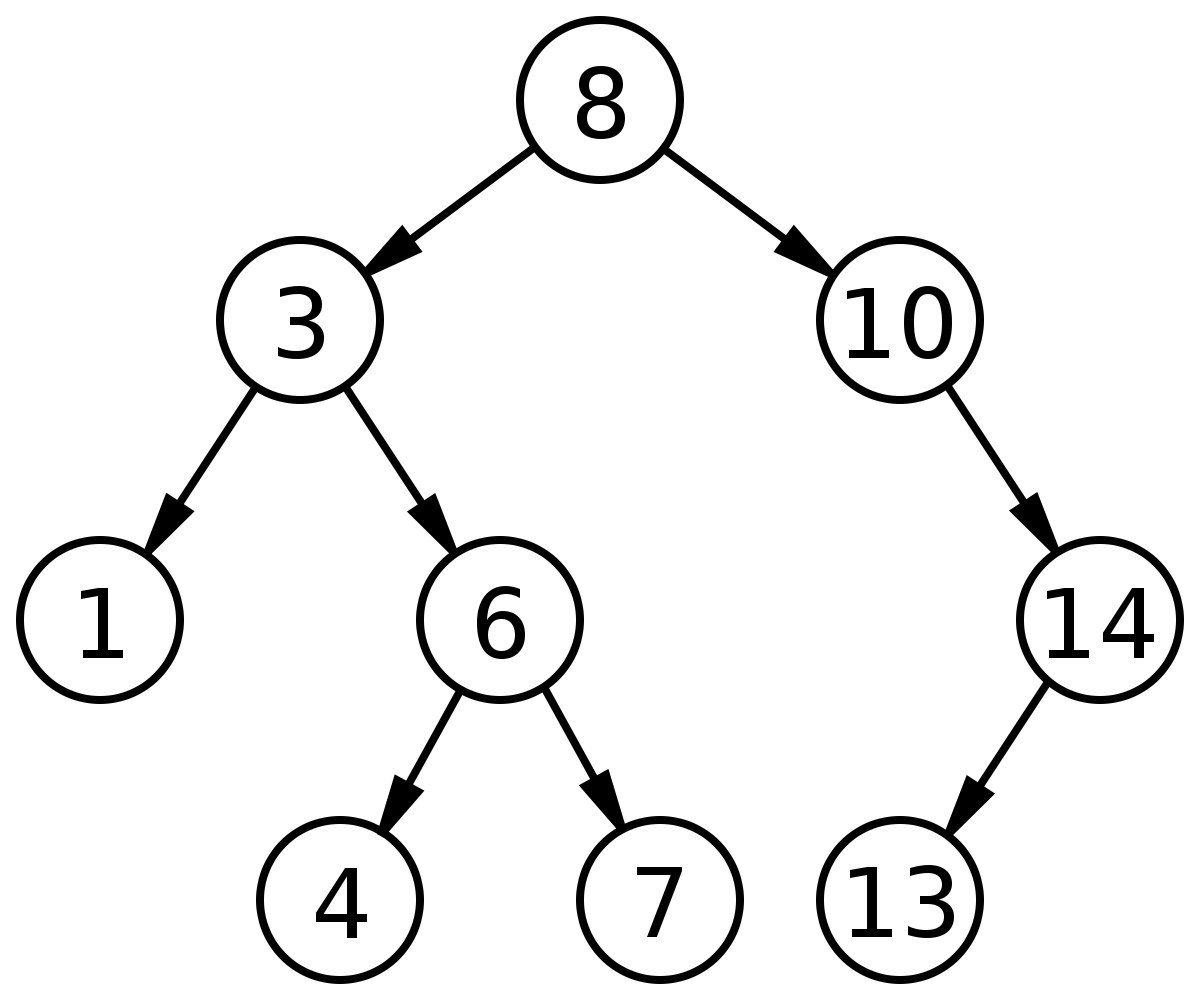
現在,這種有序的關係是非常容易看到的。 注意,根節點 8 左邊的每個值都小於 8,右邊的每個值都大於 8。 還要注意的是,這種關係也適用於每個子樹。 例如,第一個左孩子節點是一個子樹。 3 是父節點,它正好有兩個子節點——根據二進制搜索樹的規則,我們甚至不用看就知道這個節點的左子節點(以及它的任何子節點)都將小於 3,右子節點(以及它的任何子節點)都將大於 3(但也小於根結點的值),依此類推。
二叉搜索樹是非常常見且有用的數據結構,因爲它們在幾種常見操作(例如查找、插入和刪除)的平均情況下提供對數的時間複雜度。
--instructions--
我們將從簡單的內容開始。 我們在這裏定義了一個二叉搜索樹結構的骨架,此外還有一個爲我們的樹創建節點的函數。 注意觀察每個節點可能有一個左值和右值。 如果子樹存在,它們將被分配給對應的子樹。 在我們的二叉搜索樹中,你將創建一個方法來向我們的二叉搜索樹添加新的值。 該方法應該被稱爲add ,它應該接受一個整數值來添加到樹中。 注意保持二叉搜索樹的不變量:每個左子項中的值應小於或等於父值,並且每個右子項中的值應大於或等於父值。 在這裏,讓我們確保我們的樹不會含有重複的值。 如果我們嘗試添加已存在的值,則該方法應返回null 。 否則,如果添加成功,則應返回undefined 。
提示: 樹是自然的遞歸數據結構!
--hints--
存在 BinarySearchTree 的數據結構。
assert(
(function () {
var test = false;
if (typeof BinarySearchTree !== 'undefined') {
test = new BinarySearchTree();
}
return typeof test == 'object';
})()
);
二叉搜索樹應該有一個名爲 add 的方法。
assert(
(function () {
var test = false;
if (typeof BinarySearchTree !== 'undefined') {
test = new BinarySearchTree();
} else {
return false;
}
return typeof test.add == 'function';
})()
);
添加的方法應該根據二叉搜索樹的規則來添加元素。
assert(
(function () {
var test = false;
if (typeof BinarySearchTree !== 'undefined') {
test = new BinarySearchTree();
} else {
return false;
}
if (typeof test.add !== 'function') {
return false;
}
test.add(4);
test.add(1);
test.add(7);
test.add(87);
test.add(34);
test.add(45);
test.add(73);
test.add(8);
const expectedResult = [1, 4, 7, 8, 34, 45, 73, 87];
const result = test.inOrder();
return expectedResult.toString() === result.toString();
})()
);
添加一個已經存在的元素應該返回 null。
assert(
(function () {
var test = false;
if (typeof BinarySearchTree !== 'undefined') {
test = new BinarySearchTree();
} else {
return false;
}
if (typeof test.add !== 'function') {
return false;
}
test.add(4);
return test.add(4) == null;
})()
);
--seed--
--after-user-code--
BinarySearchTree.prototype = Object.assign(
BinarySearchTree.prototype,
{
inOrder() {
if (!this.root) {
return null;
}
var result = new Array();
function traverseInOrder(node) {
node.left && traverseInOrder(node.left);
result.push(node.value);
node.right && traverseInOrder(node.right);
}
traverseInOrder(this.root);
return result;
}
}
);
--seed-contents--
var displayTree = tree => console.log(JSON.stringify(tree, null, 2));
function Node(value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
function BinarySearchTree() {
this.root = null;
// Only change code below this line
// Only change code above this line
}
--solutions--
function Node(value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
function BinarySearchTree() {
this.root = null;
this.add = function(element) {
let current = this.root;
if (!current) {
this.root = new Node(element);
return;
} else {
const searchTree = function(current) {
if (current.value > element) {
if (current.left) {
return searchTree(current.left);
} else {
current.left = new Node(element);
return;
}
} else if (current.value < element) {
if (current.right) {
return searchTree(current.right);
} else {
current.right = new Node(element);
return;
}
} else {
return null;
}
};
return searchTree(current);
}
};
}