2.6 KiB
| title |
|---|
| Logical Operators |
Logical Operators
AND (&&)
A&&B returns True if both A and B are True. If either A or B (or both) are False, then A&&B is False.
| A | B | AND(A,B) |
|---|---|---|
| f | t | f |
| f | f | f |
| t | t | t |
| t | f | t |
OR (||)
A||B returns True if A or B (or both A and B) is True. Only returns False if both A and B is False.
| A | B | OR(A,B) |
|---|---|---|
| f | t | t |
| f | f | f |
| t | t | t |
| t | f | t |
NOT (!)
Returns the opposite value. Ex. if A is true, then !A is false, and if A is false, then !A is true. This is the only logical operator that works on only one input, which makes it a unary operator.
| A | B | NOT(A) | NOT(B) |
|---|---|---|---|
| f | t | t | f |
| f | f | t | t |
| t | t | f | f |
| t | f | f | t |
XOR ("eXclusive or")
Is known as exclusive or. Similar to OR, but returns False if both A and B are true. That is, XOR returns true if one and only one of A or B is True.
| A | B | XOR(A,B) |
|---|---|---|
| f | t | t |
| f | f | f |
| t | t | f |
| t | f | t |
Implication (A -> B)
Read as "if A, then B" or "A implies B".
Only returns False when A is True and B is False. Otherwise the implication is True.
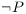
Note: Implications are often used for direct mathematical proofs. A represents the hypothesis, while B is the conclusion.
The only time the conditional is false is when a true value leads to a false value.
| A | B | IF(A,B) |
|---|---|---|
| f | t | t |
| f | f | t |
| t | t | t |
| t | f | f |
Logical Equivalence (iff: if and only if)
"P if and only if Q" is the same as "P implies Q AND Q implies P". In other words, the truth tables for P and Q are identical for all truth values.
This is known as the biconditional. It is the equivalent of A -> B AND B->A. It means that both conditionals must be satisfied in order for the biconditional to be true.
You can easily see that the out output of the IFF operator in the truth table is the same as the ANDing of columns 3 and 4.
| A | B | IF(A,B) | IF(B,A) | IFF(A,B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| f | t | t | f | f |
| f | f | t | t | t |
| t | t | t | t | t |
| t | f | f | t | f |
More Information:
+* Logical Operators in Javascript +* Logical Operators in PHP +* Logical Operators in C++